Introduction to Problem Solving
Does your company need to make major decisions on new
investments in equipment or personnel? Does your
team want to generate new product, service, process, or
marketing approaches for improving your company’s
competitive position? Do you believe that
identifying, analyzing, and solving problems is more
important than assigning blame for the achievement of
your company’s goals?
If you’ve answered yes to one or more of the above
questions, your company will benefit from understanding
and implementing formal problem solving techniques.
Our seminar program Introduction to Problem Solving will show you how to begin using formal problem solving techniques to:
![]() • Quickly identify, analyze, and solve problems
• Quickly identify, analyze, and solve problems
![]() in
any type of organization
in
any type of organization
![]() • Make better decisions based on both facts
• Make better decisions based on both facts
![]() and opinions
and opinions
![]() • Take appropriate corrective or preventive
• Take appropriate corrective or preventive
![]() actions
actions
![]() • Identify, prioritize, and implement new
• Identify, prioritize, and implement new
![]() approaches
for achieving your goals
approaches
for achieving your goals
![]() • Continuously improve your company’s
• Continuously improve your company’s
![]() products,
services,
and operations
products,
services,
and operations
Introduction to Problem Solving is oriented toward Executives, Managers, Supervisors, and Technical Professionals. The program can be customized to meet the specific needs of your industry or group.
The program consists of eight instructional units and requires approximately eight hours for presentation. Participants receive a Seminar Binder including copies of all slides, reference information, and additional materials.
Please contact us to learn how to put the techniques of formal problem solving to work at your company.
To download the data sheet for this program, please click here. (PDF)
Seminar Outline:
Unit 1 - The Problem Solving Process
![]() • Introduction
• Introduction
![]() • Key Definitions
• Key Definitions
![]() – Entity
– Entity
![]() – Defect
– Defect
![]() – Nonconformity
– Nonconformity
![]() – Nonconforming Unit
– Nonconforming Unit
![]() – Rework
– Rework
![]() – Repair
– Repair
![]() – Deviation
– Deviation
![]() – Wavier
– Wavier
![]() – Disposition
– Disposition
![]() – Corrective Action
– Corrective Action
![]() – Preventive Action
– Preventive Action
![]() • Formal Problem Solving Techniques
• Formal Problem Solving Techniques
![]() • The Steps of Problem Solving
• The Steps of Problem Solving
![]() • Choosing a Team
• Choosing a Team
![]() • Team Members
• Team Members
![]() – The “Responsible Person”
– The “Responsible Person”
![]() – The Facilitator
– The Facilitator
![]() – Subject Matter Experts
– Subject Matter Experts
![]() – Stakeholders
– Stakeholders
![]() • Choosing a Facilitator
• Choosing a Facilitator
![]() • Time Limitations
• Time Limitations
Unit 2 - Identifying the
Problem
![]() •
Stating the Problem
•
Stating the Problem
![]() •
Avoiding Assignment of Blame
•
Avoiding Assignment of Blame
![]() •
Avoiding Assumptions of Cause
•
Avoiding Assumptions of Cause
![]() •
Selecting Appropriate Tools and Techniques
•
Selecting Appropriate Tools and Techniques
Unit 3 - Analyzing the Problem
![]() • Tools and Techniques for Analysis
• Tools and Techniques for Analysis
![]() • Collecting Real Data
• Collecting Real Data
![]() • Determining Root Causes
• Determining Root Causes
![]() • Separating Analysis from Potential Solutions
• Separating Analysis from Potential Solutions
Unit 4 - Identifying Potential
Solutions
![]() • Tools and Techniques for Identifying
• Tools and Techniques for Identifying![]() Solutions
Solutions
![]() • Separating Solutions from Analysis
• Separating Solutions from Analysis
![]() • Prioritizing Solutions
• Prioritizing Solutions
Unit 5 - Implementing Solutions
![]() • Tools and Techniques for Implementing
• Tools and Techniques for Implementing
![]() Solutions
Solutions
![]() • Establishing the Plan
• Establishing the Plan
![]() • Implementing the Plan
• Implementing the Plan
![]() • Documenting Actions
• Documenting Actions
![]() • Documenting Results
• Documenting Results
Unit 6 - Evaluating Solutions
![]() • Questioning Results
• Questioning Results
![]() – Determining if the Original Problem
– Determining if the Original Problem
![]() Was Solved
Was Solved
![]() – Determining if New Problems
– Determining if New Problems
![]() Were Created
Were Created
![]() • Analyzing Benefits
• Analyzing Benefits
![]() • Starting Again
• Starting Again
Unit 7 - Tools for Problem
Solving
![]() • Brainstorming
• Brainstorming
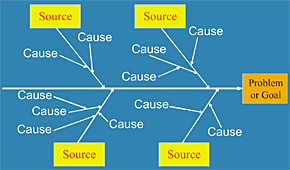
![]() • Cause and Effect Diagrams
• Cause and Effect Diagrams
![]() – Cause Enumeration Diagrams
– Cause Enumeration Diagrams
![]() – Dispersion Analysis Diagrams
– Dispersion Analysis Diagrams
![]() – Process Analysis Diagrams
– Process Analysis Diagrams
![]() • Charts and Graphs
• Charts and Graphs
![]() • Check Sheets
• Check Sheets
![]() • Control Charts
• Control Charts
![]() – Attributes Control Charts
– Attributes Control Charts
![]() – Variables Control Charts
– Variables Control Charts
![]() • Cost Benefit Analysis
• Cost Benefit Analysis
![]() • Criteria Rating
• Criteria Rating
![]() • Designed Experiments
• Designed Experiments
![]() • Flow Charts
• Flow Charts
![]() • Force Field Analysis
• Force Field Analysis
![]() • Gantt Charts and PERT Charts
• Gantt Charts and PERT Charts
![]() • Histograms
• Histograms
![]() • Pareto Charts
• Pareto Charts
![]() • Regression Analysis
• Regression Analysis
![]() • Paired Comparisons
• Paired Comparisons
![]() • Pictographs
• Pictographs
![]() • Process Maps
• Process Maps
![]() • Failure Mode and Effects Analysis
• Failure Mode and Effects Analysis
![]() • Surveys and Interviews
• Surveys and Interviews
![]() • Weighted Voting
• Weighted Voting
![]() • Additional Tools and Techniques
• Additional Tools and Techniques
Unit 8 - How to Learn More
![]() • Online Resources
• Online Resources
![]() • Books and Publications
• Books and Publications
![]() • Training Materials
• Training Materials
![]() • Consultants
• Consultants
![]() • Summary
• Summary
Secrets of Marketing | Intro to ISO 9000 | ISO 9001 Int. Auditing | Implementing Six Sigma
Send mail to websupport@iplusnet.com with questions or comments about this web site.
Copyright © 2024 by Innovations PLUS. All rights reserved.
